Augmented Reality: Transforming User Experiences
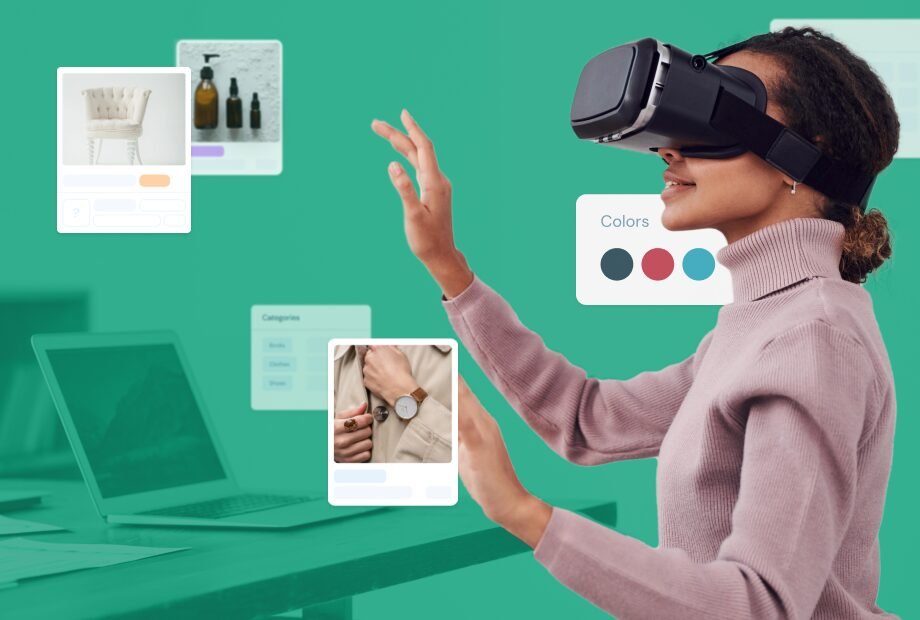
In the ever-evolving world of technology, Augmented Reality (AR) has emerged as one of the most transformative innovations, reshaping the way we interact with the digital world and enhancing real-world experiences. By overlaying digital content—such as images, sounds, and data—onto the physical environment, AR has revolutionized industries ranging from entertainment to healthcare, education, retail, and beyond. With the rapid advancements in hardware, software, and connectivity, AR is no longer a futuristic concept but a powerful tool influencing user experiences globally.
What is Augmented Reality?
At its core, Augmented Reality refers to the integration of digital content into the user’s view of the real world, thereby augmenting their sensory experience. Unlike Virtual Reality (VR), which immerses the user in a completely digital world, AR blends the digital and physical worlds, creating a hybrid environment where users can interact with both simultaneously.
This interaction is often facilitated through devices such as smartphones, tablets, smart glasses, and AR headsets. The key to AR’s effectiveness lies in its ability to seamlessly blend the virtual and real worlds, enhancing what users see, hear, and sometimes even feel, without requiring them to be fully immersed in a virtual environment.
See also: The Role of Big Data in Modern Business
How Augmented Reality Enhances User Experiences
1. Entertainment and Gaming
AR has brought a new dimension to the entertainment industry. The gaming sector, in particular, has seen a tremendous transformation through AR technology. Popular games like Pokémon GO revolutionized mobile gaming by allowing players to interact with virtual characters placed in real-world locations through their smartphones. This blend of the virtual and real worlds created an immersive and interactive experience that appealed to millions worldwide.
Beyond gaming, AR is also being used in film and television production. Movies are increasingly incorporating AR elements to engage audiences with interactive storylines and experiences that extend beyond the screen. Viewers can use AR to unlock exclusive content or participate in immersive narratives, which enhances engagement and brings stories to life in novel ways.
2. Education and Training
In education, AR offers endless possibilities for enhancing learning experiences. By overlaying educational content onto the real world, AR can turn ordinary lessons into interactive, dynamic experiences. For example, students can explore 3D models of historical landmarks, interact with virtual organisms to learn about biology, or manipulate geometric shapes in space to understand mathematical concepts.
Additionally, AR is making waves in vocational training and professional development. In fields such as medicine, engineering, and aviation, AR can be used to simulate complex procedures and situations, providing hands-on experience without real-world risks. Surgeons can practice delicate operations with AR visualizations, while mechanics can use AR-guided instructions to repair equipment more accurately.
3. Retail and E-Commerce
In the retail sector, AR is transforming the way consumers shop, making the experience more personalized and interactive. Augmented reality tools allow customers to virtually try on clothes, shoes, and accessories or see how furniture would look in their homes before making a purchase. Companies like IKEA and Warby Parker have already embraced this technology, offering virtual fitting rooms and home design tools that increase consumer confidence and reduce return rates.
Moreover, AR has also enhanced the in-store shopping experience. By scanning products with their smartphones, shoppers can access detailed product information, reviews, and even virtual demonstrations, helping them make more informed purchasing decisions.
4. Healthcare
In healthcare, AR has shown incredible promise in improving patient care and assisting medical professionals. Surgeons can use AR to view 3D visualizations of a patient’s anatomy during procedures, enhancing precision and minimizing the risks of errors. AR can also assist in physical therapy by guiding patients through rehabilitation exercises with real-time feedback on their movements.
For medical education, AR offers students a hands-on learning environment. Medical trainees can practice surgical procedures using AR simulations that mimic real-life conditions. Additionally, AR has the potential to provide patients with more personalized care. For example, it can overlay diagnostic information on a patient’s body in real time, offering insights into treatment options and helping patients better understand their conditions.
5. Tourism and Navigation
AR has the potential to redefine how we explore the world, providing tourists and travelers with enhanced, interactive experiences. By using AR, people can scan landmarks or points of interest to receive additional information such as historical facts, opening hours, and visitor reviews, all in real time. This allows for a more enriched, immersive experience while exploring new locations.
In urban navigation, AR apps are helping people find their way with ease. Navigation systems overlay directional arrows and information on the streets as users walk, providing real-time, step-by-step directions. This can significantly enhance the user experience, making it easier to navigate crowded streets or unfamiliar environments.
The Future of Augmented Reality
As technology continues to advance, the potential of Augmented Reality is boundless. Innovations in AI, 5G connectivity, and AR hardware will open new doors for interactive experiences. With the development of lighter, more affordable AR headsets and glasses, the barrier to entry will continue to lower, bringing AR into everyday life.
One area that holds tremendous promise is AR’s integration with artificial intelligence. AI-powered AR could enhance user experiences by offering real-time translations, personalized recommendations, and predictive analytics. For instance, an AI-enabled AR app could instantly translate signs or menus in foreign languages, or suggest activities based on a user’s preferences and location.
The potential for AR in industries such as real estate, automotive design, and even social media is enormous. For example, users could virtually walk through a home or car before making a purchase decision, while social platforms might allow users to create and share virtual experiences with others, further blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its enormous potential, there are several challenges that must be addressed for AR to fully transform user experiences. One of the primary hurdles is privacy and security concerns. The use of AR often involves collecting and processing vast amounts of personal data, including location tracking, facial recognition, and other sensitive information. Protecting this data and ensuring user privacy will be critical as AR becomes more integrated into daily life.
Additionally, the technology itself is still evolving. While AR applications are increasingly sophisticated, there is still a need for more powerful, compact, and affordable AR hardware to reach mass adoption. As the technology becomes more widespread, developers must also consider accessibility, ensuring that AR is inclusive and beneficial for users with disabilities.
Conclusion
Augmented Reality is quickly becoming a game-changer in how users interact with both the physical and digital worlds. From entertainment and gaming to healthcare and education, AR is enhancing experiences in ways that were previously unimaginable. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect AR to become a central part of our daily lives, enabling more immersive, personalized, and engaging interactions. However, for AR to realize its full potential, challenges related to privacy, hardware, and accessibility must be addressed. The future of AR is undoubtedly bright, and its ability to transform user experiences across industries is limitless.